Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (40): 6419-6424.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.40.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Extended trochanteric osteotomy combined with long-stem cementless prosthesis in hip revision
Zhou Wei, Liu Dong-hai, Xu Zhen-wei, Wu Deng-ke, Zhao Shi-yang
- Department of Osteoarthrosis, Pingdingshan First People’s Hospital, Pingdingshan 467000, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2014-08-22Online:2014-09-24Published:2014-09-24 -
About author:Zhou Wei, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Osteoarthrosis, Pingdingshan First People’s Hospital, Pingdingshan 467000, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Wei, Liu Dong-hai, Xu Zhen-wei, Wu Deng-ke, Zhao Shi-yang. Extended trochanteric osteotomy combined with long-stem cementless prosthesis in hip revision[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(40): 6419-6424.
share this article
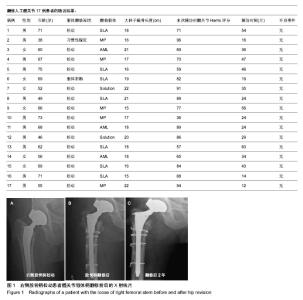
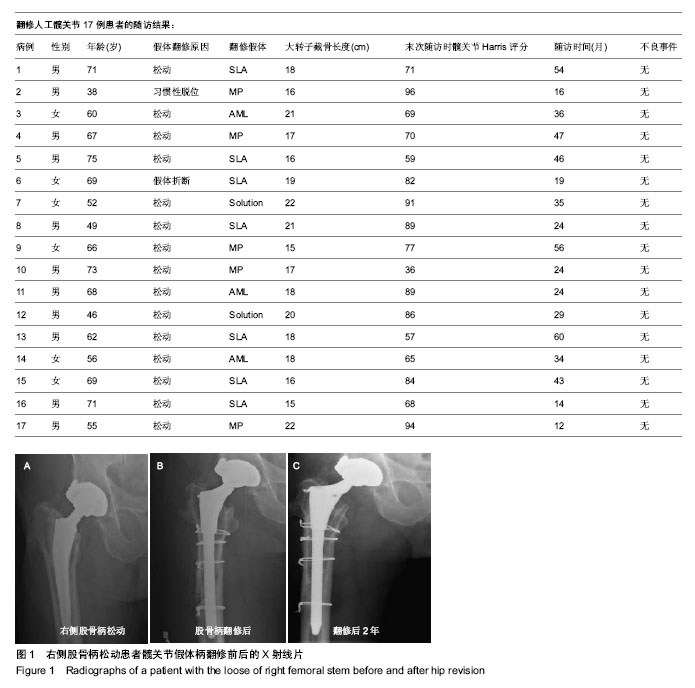
2.1 参与者数量分析 按意向性处理,纳入患者17例17髋,全部进入结果分析,无脱落。 2.2 随访结果 随访12-60个月。本组患者治疗前平均髋关节功能评分为(39.0±13.6)分(10-84分),在随访期末,平均髋关节Harris评分提高到(75.0±14.9)分(36-96分),差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01)。大转子截骨长度平均17 cm (15-23 cm),股骨柄远端和髓腔接触面的长度平均6.4 cm (4-11 cm),截骨处远端至假体末端的长度平均11.5 cm (8-18.5 cm)。 有2例假体柄出现了下沉,下沉3 mm及5 mm,X射线片上无明显透亮带形成,无临床及放射学松动迹象,在随访1年时假体柄均稳定,出现下沉病例中假体柄和髓腔接触面长度5 cm及6 cm,无下沉病例中假体柄和髓腔接触面长度(6.6±2.1) cm(4-11 cm);出现下沉病例中截骨处远端至假体末端长度7 cm及11 cm,无下沉病例中截骨处远端至假体末端长度(11.8±2.76) cm(6.5-18.5 cm)。 2.3 典型病例 男性患者,68岁,翻修前出现右髋关节及大腿上段疼痛,因疼痛已扶拐杖助行,翻修前检查发现股骨侧假体柄出现松动,行股骨侧髋关节假体柄翻修,治疗后2年随访,未诉特殊不适症状,Harris评分89分。翻修前后X射线片见图1。 2.4 不良事件 术中未出现截骨时股骨干骨折,未出现截骨块滑移,术中未因铰刀扩髓出现股骨干穿孔,所有的截骨块都用钢丝捆扎,其中2例应用同种异体皮质骨块行近端加强。17例患者截骨块均固定良好,假体周围骨质未见明显吸收、溶解,未出现深部感染、切口感染、深静脉血栓形成等并发症,随访期末无再次翻修病例。"
| [1] 廖全明,裴洪,王克军.髋关节翻修手术技巧探讨[J].中国骨与关节外科杂志,2013,6(1):61-63.
[2] 裴福兴,康鹏德.髋关节翻修相关问题[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2010,25(4):377-378.
[3] Chen AF, Hozack WJ. Component selection in revision total hip arthroplasty.Orthop Clin North Am.2014;45(3):275-286.
[4] Miner TM,Momberger NG,Chong D,et al .The extended trochanteric osteotomy in revision hip arthroplasty:a critical review of 166 cases at mean 3-year,9-month follow-up.J Arthroplasty.2001;16(8):s188-s194.
[5] Canale ST, Beaty JH. 坎贝尔骨科手术学[M].12版.北京:人民军医出版社,2013:254-261.
[6] Mardones R,Gonzalez C,Cabanela ME,et al. Extended femoral osteotomy for revision of hip arthroplasty:results and complications. J Arthroplasty.2005; 20(1):79 -83.
[7] Paprosky WG,Sporpe SM.Controlled femoral fracture:easy in. J Arthroplasty.2003; 18(3):S91-S93.
[8] MacDonald SJ,Cole C,Guerin J,et al. Extended trochanteric osteotomy via the direct lateral approach in revision hip arthroplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; 417(10):210-216.
[9] Lerch M,Lewinski G,Windhagen H,et al.Revision of total hip arthroplasty:clinical outcome of extended trochanteric osteotomy and intraoperative femoral fracture. Technol Health Care.2008;16(4):293-300.
[10] Levine BR,Della valle CJ,Lewis P. Extended femoral osteotomy for the treatment of Vancouver B2/B3 periprosthetic fracture of the femur. J Arthroplasty. 2008; 23 (4):527-533.
[11] Morshed S,Huffman GR,Ries MD. Extended trochanteric osteotomy for 2-stage revision of infected total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty.2005;20(3):294-301.
[12] Levine BR,Della Valle CJ,Hamming M,et al.Use of the extended trochanteric osteotomy in treating prosthetic hip infection. J Arthroplasty.2009;24(1):49-55.
[13] Böhm P, Bischel O.The use of tapered stems for femoral revision surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2004; 420(3): 148-159.
[14] Engh CA Jr, Hopper RH Jr, Engh CA Sr. Distal ingrowth components. Clin Orthop Relat Res .2004;420(3):135-141.
[15] Krishnamurthy AB, MacDonald SJ, Paprosky WG.5- to13-year follow-up study on cementless femoral components in revision surgery. J Arthroplasty.1997; 12 (8): 839-847.
[16] McAuley JP, Engh CA Jr.Femoral fixation in the face of considerable bone loss: cylindrical and extensively coated femoral components. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2004; 429(10): 215-221.
[17] Sporer SM, Paprosky WG. Revision total hip arthroplasty: the limits of fully coated stems. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2003; 417(10):203-209.
[18] Engh CA, Massin P, Suthers KE.Roentgenographic assessment of the biologic fixation of porous-surfaced femoral components. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; 257 (8): 107-128.
[19] Itasaka T,Kawai A,Sato T,et al.Diagnosis of infection after total hip arthroplasty.J Orthop Sci.2001;6(4):320-326.
[20] Stemheim A,Abolghasemian M,Safir OA,et al. A long-term survivorship comparison between cemented and uncemented cups with shelf grafts in revision total hip arthroplasty after dysplasia.J Arthroplasty, 2013;28(2):303-308.
[21] Pattyn C,Audenaert E. Early complications after revision total hip arthroplasty with cemented dual-mobility socket and reinforcement ring.Acta Orthop Belg. 2012; 78(3): 357-361.
[22] Weiss RJ,Stark A,Karrholm J. A modular cementless stem vs. cemented long-stem prostheses in revision surgery of the hip: a population-based study from the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop. 2011;82(2):136-142.
[23] Jibodh SR,Schwarzkopf R,Anthony SG,et al. Revision hip arthroplasty with a modular cementless stem: mid-term follow up.J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(7):1167-1172.
[24] Pelt CE,Madsen W,Erickson JA,et al. Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty With a Modular Cementless Femoral Stem.J Arthroplasty. 2014;9 [Epub ahead of print].
[25] Imbuldeniya AM,Walter WK,Zicat BA,et al.The S-ROM hydroxyapatite proximally-coated modular femoral stem in revision hip replacement: results of 397 hips at a minimum ten-year follow-up.Bone Joint J.2014;96-B(6):730-736.
[26] Goodman S, Pressman A, Saastamoinen H,et al.Modified sliding trochanteric osteotomy in revision total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty.2004; 19(8):1039-1041.
[27] Lakstein D, Safir O, Backstein D, et al.Modified trochanteric slide for complex hip arthroplasty: clinical outcomes and complication rates. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(3):363-368.
[28] Bal BS, Kazmier P, Burd T, et al.Anterior trochanteric slide osteotomy for primary total hip arthroplasty. Review of nonunion and complications. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(1): 59-63.
[29] Ebraheim NA, Patil V, Liu J,et al.Sliding trochanteric osteotomy in acetabular fractures: a review of 30 cases. Injury. 2007;38(10):1177-1182.
[30] Baba T, Shitoto K.Revision of total hip arthroplasty using the Kerboull and KT plates. Int Orthop.2010;34(3):341-347.
[31] Haler NP, Hick GG, Karrholm J. Uncemented and cemented primary total hip arthroplasty in the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register:Evaluation of 170,413 operations.Acta Orthop. 2010; 81(1):34-41.
[32] Mertl P, Philippot R, Rosset P, et al. Distal locking stem for revision femoral loosening and peri-prosthetic fractures. Int Orthop. 2011;35(2):275-282.
[33] Salemyr MF, Sktildenberg OG, Bod6n HG, et al.Good results with anuncemented proximally HA-coated stem in hip revision surgery: 62hips followed for 2-13 years. Acta Orthop. 2008; 79(2):184-193.
[34] 王龙强,王黎明,唐成,等.非骨水泥型广泛涂层长柄假体在髋关节翻修股骨轻中度缺损重建中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011;15(30):5547-5551.
[35] 蒋林,李舰,简小飞,等.股骨侧远端生物固定假体在高龄患者全髋关节翻修中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(43):8042-8045.
[36] Neumann D, Dueckelmann L, Thaler C,et al. Revision total hip arthroplasty using a cementless tapered revision stem in patients with a mean age of 82 years. Int Orthop. 2012;36(5): 961-965.
[37] Mokka J, Keemu H, Koivisto M,et al. Experience of Structural Onlay Allografts for the Treat ment of Bone Deficiency in Revision Total HIP Arhroplasty. Scand J Surg.2013;102(4): 265-270.
[38] Rogers BA, Sternheim A, Backstein D, et al.Proximal Femoral Allograft forMajor Segmental Femoral Bone Loss: A Systematic Literature Review. Adv Orthop.2011;13(10): 4061-4068.
[39] Prokopetz JJ, Losina E, Bliss RL, et al. Risk factors for revision of primary total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2012;15(10):251-264.
[40] Kosashvili Y, Drexler M, Backstein D. Dislocation after the first and multiple revision total hip arthroplasty: comparison between acetabulum-only, femur-only and both component revision hip arthroplasty. Can J Surg.2014;57(2): E15-E18. |
| [1] | Liang Xin, Wang Heng, Li Xian-rong. Preoperative application of alprazolam for patients with anxiety and depression and pain after total knee arthroplasty: its safety and effectiveness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 985-992. |
| [2] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [3] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [4] | Lu Yao-jia, Xiong Chuan-zhi, Li Xiao-lei, Hu Han-sheng, Chen Gang, Wang Qiang, Lu Zhi-hua. Comparison of two methods for reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1004-1008. |
| [5] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [6] | Chen Qun-qun, Qiao Rong-qin, Duan Rui-qi, Hu Nian-hong, Li Zhao, Shao Min. Acu-Loc®2 volar distal radius bone plate system for repairing type C fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1025-1030. |
| [7] | Ye Xiang-yang, Sun Xiang, Tang Li-xin, Zhen Ping, Geng Bin, Wang Hua-lei, Zhao Yu-guo. Acetabular liner wear of cross-linked versus conventional polyethylene for total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1143-1148. |
| [8] | Tian Hai-tao, Wang Yuan-he, Tian Shao-qi, Zhang Xu-teng, Sun Kang. Effects and safety assessment of methylprednisolone on postoperative nausea and vomiting and pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 335-339. |
| [9] | Jia Jin-ling, Dong Yu-zhen. Finite element analysis of prosthesis position during hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 401-405. |
| [10] | Zhu Shi-bai, Zhai Jie, Jiang Chao, Ye Can-hua, Chen Xi, Weng Xi-sheng, Qian Wen-wei. Application of “enhanced recovery after surgery” in the perioperative period of total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 456-463. |
| [11] | Wei Zhi-hui, Zhang Zhong-zu, Zhang Ming-hua. Intravenous combined with topical application of tranexamic acid in primary total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of efficacy and safety [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 464-470. |
| [12] | Hu Jun, Zhang De-qiang, Tang Xin. Postoperative quality of life of internal fixation versus hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 2953-2960. |
| [13] | Sun Hao, Wei Jun-qiang, Liu Li-rui, Yan Shi, Jin Yu, Feng Zhen. Time of lower extremity deep venous thrombosis after hip arthroplasty in senile patients with osteoporotic femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 2961-2965. |
| [14] |
Gao Wei-lu, Li Hong, Liu Bi-quan, Hu Yong, Liu Jing-jun, Yin Li, Liu Hu, Mei Bin, Yin Zong-sheng.
Analgesic effect of femoral and sciatic nerve block under multimodal analgesia in total knee arthroplasty
|
| [15] | Bai Zhao-hui, Zhang Ying, Yin Qing-shui, Xia Hong, Wang Jian-hua, Xu Jun-jie. Navigational template applied in the orthopaedic field in China: a bibliometric analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 3023-3030. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||